Coursera: Neural Networks and Deep Learning (Week 1) Quiz [MCQ Answers] - deeplearning.ai
These solutions are for reference only.
It is recommended that you should solve the assignment and quiz by yourself honestly then only it makes sense to complete the course.
but if you cant figure out some part of it than you can refer these solutions
make sure you understand the solution
dont just copy paste it
answers in green colour
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
▸ Introduction to deep learning :
These solutions are for reference only.
It is recommended that you should solve the assignments and quizes by yourself honestly then only it makes sense to complete the course.
but if you are stuck in between refer these solutions
make sure you understand the solution
dont just copy paste it
answers in green colour
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
It is recommended that you should solve the assignments and quizes by yourself honestly then only it makes sense to complete the course.
but if you are stuck in between refer these solutions
make sure you understand the solution
dont just copy paste it
answers in green colour
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- What does the analogy “AI is the new electricity” refer to?
- AI runs on computers and is thus powered by electricity, but it is letting computers do things not possible before.
- Similar to electricity starting about 100 years ago, AI is transforming multiple industries.
(AI is transforming many fields from the car industry to agriculture to supply-chain...) - Through the “smart grid”, AI is delivering a new wave of electricity.
- AI is powering personal devices in our homes and offices, similar to electricity.
- Which of these are reasons for Deep Learning recently taking off? (Check the three options that apply.)
- Deep learning has resulted in significant improvements in important applications such as online advertising, speech recognition, and image recognition.
(These were all examples discussed in lecture 3.) - Neural Networks are a brand new field.
- We have access to a lot more computational power.
( The development of hardware, perhaps especially GPU computing, has significantly improved deep learning algorithms' performance.) - We have access to a lot more data.
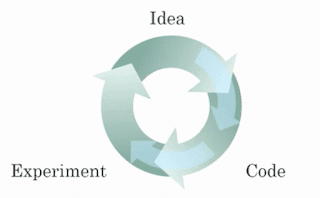
(The digitalization of our society has played a huge role in this.) - Recall this diagram of iterating over different ML ideas. Which of the statements below are true? (Check all that apply.)
- Being able to try out ideas quickly allows deep learning engineers to iterate more quickly.
- Faster computation can help speed up how long a team takes to iterate to a good idea.
- It is faster to train on a big dataset than a small dataset.
- Recent progress in deep learning algorithms has allowed us to train good models faster (even without changing the CPU/GPU hardware).
- When an experienced deep learning engineer works on a new problem, they can usually use insight from previous problems to train a good model on the first try, without needing to iterate multiple times through different models. True/False?
- True
- False
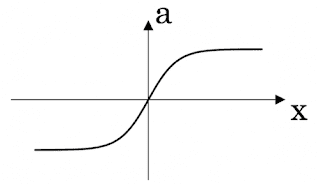
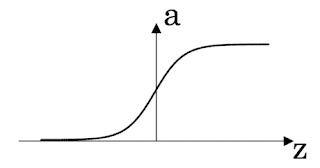
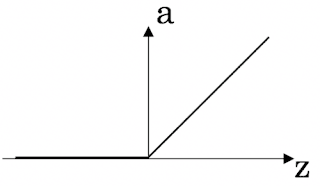
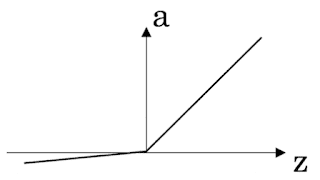
(Finding the characteristics of a model is key to have good performance. Although experience can help, it requires multiple iterations to build a good model.) - Which one of these plots represents a ReLU activation function?
- Figure 1:
- Figure 2:
- Figure 3: (This is the ReLU activation function, the most used in neural networks.)
- Figure 4:
- Images for cat recognition is an example of “structured” data because it is represented as a structured array in a computer. True/False?
- True
- False
( Images for cat recognition is an example of “unstructured” data.) - A demographic dataset with statistics on different cities' population, GDP per capita, economic growth is an example of “unstructured” data because it contains data coming from different sources. True/False?
- True
- False
(A demographic dataset with statistics on different cities' population, GDP per capita, economic growth is an example of “structured” data by opposition to image, audio or text datasets.)- Why is an RNN (Recurrent Neural Network) used for machine translation, say translating English to French? (Check all that apply.)
- It can be trained as a supervised learning problem.
(We can train it on many pairs of sentences x (English) and y (French).) - It is strictly more powerful than a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN).
- It is applicable when the input/output is a sequence (e.g., a sequence of words).
( An RNN can map from a sequence of english words to a sequence of french words.) - RNNs represent the recurrent process of Idea->Code->Experiment->Idea->....
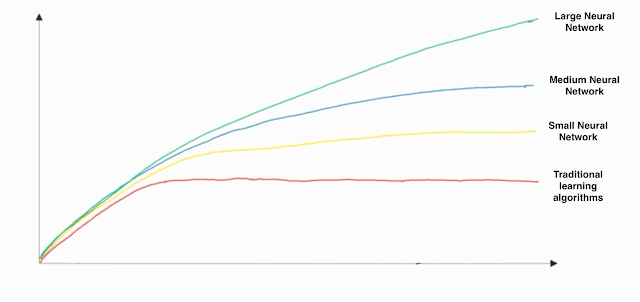
- In this diagram which we hand-drew in lecture, what do the horizontal axis (x-axis) and vertical axis (y-axis) represent?
- x-axis is the amount of data
y-axis (vertical axis) is the performance of the algorithm. - x-axis is the performance of the algorithm
y-axis (vertical axis) is the amount of data. - x-axis is the amount of data
y-axis is the size of the model you train. - x-axis is the input to the algorithm
y-axis is outputs. - Assuming the trends described in the previous question's figure are accurate (and hoping you got the axis labels right), which of the following are true? (Check all that apply.)
- Decreasing the training set size generally does not hurt an algorithm’s performance, and it may help significantly.
- Increasing the training set size generally does not hurt an algorithm’s performance, and it may help significantly.
(Bringing more data to a model is almost always beneficial.) - Increasing the size of a neural network generally does not hurt an algorithm’s performance, and it may help significantly.
( According to the trends in the figure above, big networks usually perform better than small networks.) - Decreasing the size of a neural network generally does not hurt an algorithm’s performance, and it may help significantly.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
main course coursera.org



No comments